Primary Protection: The History of the Pill
This little gal has gone through quite the journey.
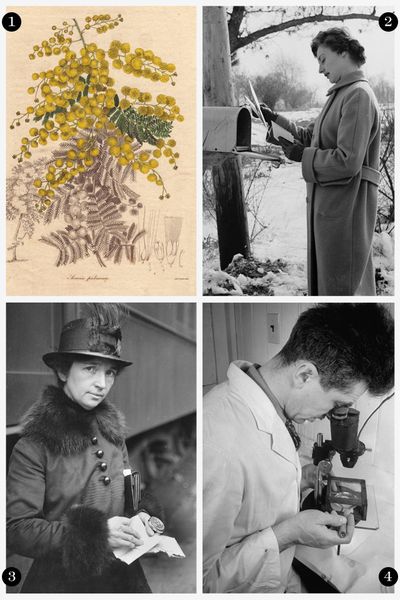

1. Early Innovation, Ancient Egypt:
Before any oral contraceptives were introduced, Ancient Egyptian women took on the task of sexual protection themselves. They used cotton, dates, honey and acacia as a suppository, which when fermented, has a spermicidal effect.
2. Privacy, Please, 1873:
The passing of the Comstock Act prohibited advertisements, information, and distribution of birth control and allowed the postal service to confiscate contraceptive devices sold through the mail. This created a major hurdle for any further medical advances.
3. A Rightful Concern, 1914 – 1936:
Margaret Sanger founded the American Birth Control League (later becoming Planned Parenthood), dedicating her life to the cause. She helped file a lawsuit that led the Court to rule that the federal government could not interfere with doctors providing contraception to their patients.
4. Work in Progress, 1951:
Tired of waiting for science to comply, Sanger sought out a team to make birth control as easy as taking an aspirin. Gregory Pincus supplied the medical expertise, while Katherine McCormick, a women's rights activist and heiress to a fortune, funded the research. Their trial run in Puerto Rico proved the pill successful in blocking ovulation.
5. Halfway There, 1957:
Mission accomplished — almost. The FDA approved the pill, but only for severe menstrual disorders, not as a contraceptive. In turn, an unusually large number of women reported having such disorder, making it clear accessible birth control should be a priority.
6. Victory at Last, 1960:
Finally, the FDA approved the first oral contraceptive, Enovid, beginning a new sexual revolution for women. The pill, like it is often seen today, represented women's rights and a generational change — the freedom to enjoy sex and make choices regarding doing so.
7. Trouble Brews, 1965:
With success came controversy — despite 6.5 million women being on the pill in just its first five years, the Pope and the Catholic Church remained against the pill. Barbara Seaman also published The Doctor's Case Against the Pill, exposing side effects of the pill, including risk of blood clots, heart attack, stroke, depression, weight gain and loss of libido. By 1979, sales dropped by 24 percent.
Get exclusive access to fashion and beauty trends, hot-off-the-press celebrity news, and more.
8. The New Era, 1988:
The original high-dose pill was taken off the market as the FDA showed health benefits from newer versions of the pills — these include a decreased risk of ovarian cancer, iron deficiency anemia and pelvic inflammatory disease. This more closely resembled the pill we know today.
9. A Way of Life, 2000:
Working women, rejoice: The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission ruled that prescription contraception must be covered by health insurance offered by employers. Further medical developments occur, like Seasonale, giving women only four periods a year, and Lybrel, eliminating periods completely.
10. Still Fighting, 2014:
Over fifty years since its original FDA approval, over 100 million women are taking this tiny tablet daily. But opposition still remains, with some companies challenging the Affordable Care Act's contraceptive mandate, which requires insurance policies to cover birth control without a copay (despite most insurance covering Viagra). Still, the pill lives up to Sanger's original version — giving women control.
Photo Credits: Getty Images